Data is continuously generated, refined, and distributed across diverse systems and applications. Yet, most organizations struggle with building a high-quality data pipeline infrastructure that can unify streaming and batch data remains one of the biggest challenges for modern organizations. Legacy models depend on manual refreshes, complex dependencies, and time-consuming ETL processes. As a result, businesses often find themselves working with outdated insights and missing critical opportunities.
Snowflake Dynamic Tables changed that narrative. They help in automation, intelligent refresh, and real-time adaptability. They update themselves as source data changes, eliminating manual orchestration and empowering teams to focus on analysis rather than maintenance. This innovation simplifies data management and transformation.
In this blog, we explore what dynamic tables are, the challenges they solve, how Snowflake provides an effective approach, key industry use cases, and best practices for effective implementation.
What are Dynamic Tables?
A dynamic table can change or update automatically, either in response to user interaction or by independently refreshing based on underlying data changes. Unlike traditional tables that require manual refreshes or scheduled ETL jobs, dynamic tables continuously update themselves based on the underlying source data. It avoids the need to create intermediate staging tables or orchestrate complex refresh schedules, as the platform handles them automatically. The dynamic table adjusts, keeping the data current according to a defined refresh interval, in case of changes in the base tables. In Snowflake, it is a data pipeline object defined by a query that continuously updates its materialized (stored) data as source data changes. This helps to simplify data transformation and management. Essentially, they combine the convenience of automated updates with the flexibility of SQL-based transformations, allowing teams to focus on insights rather than pipeline maintenance.
Why Leverage Dynamic Tables?
Dynamic tables function as the main element within a data pipeline that provides an automated and efficient way to handle data transformations. They remove the complexity of managing multiple dependent transformation tasks and streamline the data engineering workflow. Dynamic tables empower businesses for-
Real-Time Data Analytics: Dynamic tables enable businesses to access up-to-the-minute data without manual intervention. Business users can run queries that always reflect the latest information. It is helpful for dashboards, operational reporting, or decision-making scenarios.
Simplifies ETL Pipelines: Traditional ETL processes include extracting raw data, transforming it into intermediate tables, and loading the data. With dynamic tables, you can eliminate this and directly transform source data automatically. This reduces operational complexity and makes data pipeline management easier.
Frequent Data Updates: In systems like sales transactions, IoT device logs, or customer interactions, data changes frequently. Using dynamic tables ensures transformed datasets remain accurate and current. This is essential for real-time monitoring, anomaly detection, and timely reporting to avoid missed opportunities or inaccurate insights.
Cost Efficiency: Automating updates with dynamic tables reduces the need for repeated manual refreshes and custom scripts. This helps organizations gain real-time analytics without the traditional overhead associated with constant updates.
Streamlined Data Management: Dynamic tables are the best choice for modern data architectures, as they require agility, automation, and scalability. They integrate seamlessly with Snowflake features like Streams and Tasks, allowing teams to create fully automated and event-driven pipelines.
The Challenge with Traditional Data Pipelines
Building and managing robust data pipelines is a complex task. Data is spread across multiple systems, in different formats, and is often inconsistent or incomplete. Traditional data pipelines depend on series of steps ETL (Extract, Transform, Load), which is time-consuming and difficult to manage. These steps require manual orchestration, including scheduling jobs, managing dependencies, and updating intermediate tables. This creates operational complexity, increases errors, and lacks important insights. As data volumes grow, pipelines must handle increasing load without introducing latency or errors. Traditional ETL solutions struggle to scale efficiently while keeping costs under control.
Incremental data processing is one major challenge. Using it is difficult to build a scalable, performant, and cost-effective data engineering pipeline. It includes a huge manual process of identifying changes and updating results, which only increases operational complexity. Another challenge is maintaining consistency and quality across multiple tables in data transformation. Errors in one step can affect the entire pipeline, requiring additional monitoring, debugging, and reprocessing. It requires creating an efficient schedule that takes into account the dependencies and desired data freshness.
How Snowflake Dynamic Tables Solve These Challenges
Snowflake Dynamic Tables helps businesses address traditional data pipeline challenges. It empowers you by automating, optimizing, and simplifying complex data transformations. They help data engineers to define transformations using SQL queries, and Snowflake handles the materializing process and refreshing tables automatically. This eliminates the need for managing a web of streams, tasks, or manual orchestration, so that engineers focus more on logic and business value. The key capabilities of Snowflake dynamic tables include-
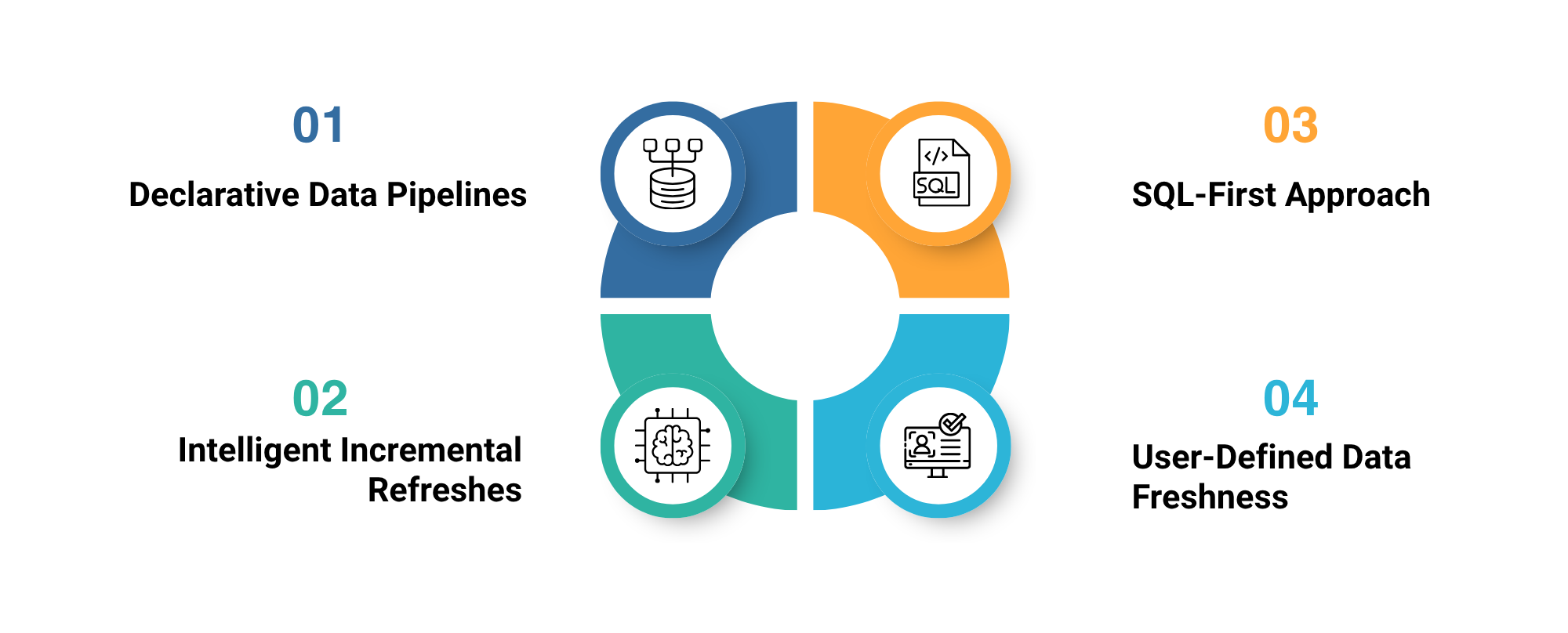 Declarative Data Pipelines
Declarative Data Pipelines
Dynamic Tables enable a fully declarative approach to building data pipelines. Data engineers can define the final output of a pipeline with a SQL query; this eliminates manual schedule or orchestrates multiple tasks. Tables can select data from regular Snowflake tables or other Dynamic Tables, forming a directed acyclic graph (DAG) of transformations. Dynamic Tables has broad support for SQL and Python; Snowflake also allows clients to use the language of their choice. This approach removes the complexity of managing streams, tasks, and data pipelines.
SQL-First Approach
Dynamic Tables often rely on SQL, so teams can reuse their existing transformation logic with some changes. Any SQL query, including aggregations, joins, and other constructs, can define the transformation. This approach ensures familiarity for engineers while supporting complex transformations across multiple tables. It also enables easy migration of legacy pipelines or lift-and-shift existing workflows without rebuilding the whole process.
Intelligent Incremental Refreshes
Snowflake dynamic tables perform an automatic incremental refreshment process. Instead of reprocessing entire datasets, only the data that has changed is refreshed, even for complex queries. This reduces computational overhead, lowers costs, and ensures timely data availability. Snowflake manages the refresh process, ensuring the table is updated according to a defined lag time. Dynamic Tables can also intelligently determine when a full refresh is required, or else skip refreshes entirely. This removes the need for manual intervention in scheduling or dependency management.
User-Defined Data Freshness
With dynamic tables, engineers can define a target lag, controlling how close or accurate data needs to be in real-time. This flexibility balances performance, cost, and freshness. Teams can deliver data to consumers as fresh as one minute from arrival while avoiding unnecessary computational expenses. This makes data pipelines both responsive and cost-efficient.
Snowflake Dynamic Tables combine all these features and help to build scalable, cost-effective, and low-maintenance pipelines. They eliminate manual orchestration, reduce computational costs, and provide consistent, up-to-date data for analytics, reporting, and business intelligence.
Common Use Cases of Snowflake Dynamic Tables
Dynamic tables in Snowflake enable a wide range of real-time data processing and analytics capabilities across various industry domains.
Financial Services Use for Risk Management and Fraud Detection
In the financial sector, data latency can mean the difference between profit and loss. Dynamic Tables enable financial services to maintain continuously updated datasets for transactions, customer activity, and market data. It helps to detect fraudulent transactions and automatically refresh data pipelines that monitor such activities. Businesses can also update credit scoring models and risk dashboards without manually managing batch refreshes.
Manage Patient Data Integration in Healthcare
Healthcare organizations need quality and accurate data for patient care, research, and clinical trials. By using dynamic tables, payers and providers can simplify data migration from multiple systems such as EHRs and IoT-enabled medical devices. It helps to keep patient health records synchronized for better patient care. Enable predictive analytics for patient outcomes by constantly updating data on vitals, lab results, and treatment responses. They also provide real-time insights into decision-making and health outcomes.
Retail – Inventory and Customer Behavior Insights
In retail, analyzing consumer trends, managing inventory, and optimizing promotions are essential. Dynamic tables help to operate with live insights across these areas. Businesses can sync sales, returns, and stock data across stores and online platforms for accurate inventory visibility. They can effectively analyze customer interactions and buying patterns to personalize offers and pricing strategies. Automating data refresh reduces latency, enables smarter merchandising, and drives success.
Manufacturing – Predictive Maintenance and Production Optimization
The manufacturing sector gets massive volumes of data from sensors, machines, and production lines. Using dynamic tables helps transform this data into actionable insights without managing ETL tasks. This data helps to accurately monitor equipment performance and predict and prevent machinery failures. Combine streaming data from production lines with ERP data to optimize production schedules and reduce downtime. As a result, dynamic tables allow manufacturers to batch data and use efficient production systems.
Best Practices for Implementing Dynamic Tables
Define Data Freshness: As organizations generate huge amounts of data, not all of them need real-time updates. So, identify which use cases truly require low latency. Setting the right target lag increases performance and cost efficiency.
Optimize Queries: The query defining a dynamic table executes during every refresh. Optimize these queries, simplify logic, eliminate unnecessary joins, and test performance before turning queries into Dynamic Tables.
Incremental Processing: Ensure your data model supports incremental updates that include timestamps or change-tracking fields. This approach minimizes full refreshes, saving time and resources.
Manage Task Billing: Consolidate or batch transformations where possible to reduce the number of task executions. Review task schedules regularly to prevent excessive runs that drive up costs
Data Integrity and Governance: Apply role-based access, data masking, and encryption to protect sensitive information. Monitor the credit usage of your dynamic tables to manage costs effectively by using Snowflake’s built-in tools.
Conclusion
Snowflake Dynamic Tables marks a significant step forward in modern data engineering. They transform how organizations design, maintain, and scale their data pipeline. With Snowflake’s Dynamic Tables, data engineers can focus more on innovations and deliver consistent, fresh, and actionable insights across every business function. A successful data strategy is about making data dynamic, responsive, and ready for action. Partnering with Kasmo, you can modernize your data infrastructure, implement best practices, and unlock the full potential of Snowflake’s data cloud to drive smarter, faster, and more scalable business outcomes.





